Whitening transformation
The whitening transformation is a decorrelation method that converts the covariance matrix S of a set of samples into the identity matrix I. This effectively creates new random variables that are uncorrelated and have the same variances as the original random variables. The method is called the whitening transform because it transforms the input matrix closer towards white noise.
This can be expressed as 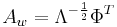 [1]
[1]
where 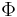 is the matrix with the eigenvectors of "S" as its columns and
is the matrix with the eigenvectors of "S" as its columns and 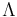 is the diagonal matrix of corresponding eigenvalues.
is the diagonal matrix of corresponding eigenvalues.
See also
References
http://courses.media.mit.edu/2010fall/mas622j/whiten.pdf
- ^ R.O. Duda, P.E. Hart, and D.G. Stork, Pattern Classification, New York: John Wiley & Sons, 2001, pp. 34